


Local Government: Municipal Systems Act, 2000 (Act No. 32 of 2000)RegulationsLocal Government: Regulations on Appointment and Conditions of Employment of Senior ManagersAnnexuresAnnexure A : Local Government: Competency Framework for Senior Managers |
ANNEXURE A
LOCAL GOVERNMENT: COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK FOR SENIOR MANAGERS
1. Definitions
In this framework—
"core competencies" are competencies that cut across all levels of work in a municipality and enhance contextualised leadership that guarantees service delivery impact; and
"leading competencies" means competencies that are required to develop clear institutional strategy, initiate, drive and implement programs to achieve long-term sustainable and measurable service delivery performance results.
| 2. | Competency Framework |
| 2.1 | This competency framework replaces regulation 26(8) of the Local Government: Municipal Performance Regulations for Municipal Managers and Managers directly accountable to Municipal Managers, (Government Notice No. 805) as published in Government Gazette No. 29089 of 1 August 2006. |
| 2.2 | A person appointed as a senior manager must have the competencies as set out in this framework. Focus must also be placed on the following key factors: |
| (a) | Critical leading competencies that drive the strategic intent and direction of local government; |
| (b) | Core competencies which senior managers are expected to possess, and which drive the execution of the leading competencies; and |
| (c) | The eight Batho Pele principles. |
| 2.3 | The competency framework consists of six leading competencies which comprise of twenty (20) driving competencies that communicate what is expected for effective performance in local government. |
| 2.4 | The competency framework further involves six (6) core competencies that act as drivers to ensure that the leading competencies are executed at an optimal level. |
| 2.5 | There is no hierarchical connotation to the structure and all competencies are essential to the role of a senior manager to influence high performance. All competencies must therefore be considered as measurable and critical in assessing the level of a senior manager's performance. |
| 2.6 | The competency framework is underscored by four (4) achievement levels that act as benchmark and minimum requirements for other human capital interventions, which are, recruitment and selection, learning and development, succession planning, and promotion. |
| 3. | Competency Framework Structure |
The competencies that appear in the competency framework are detailed below.
|
LEADING COMPETENCIES |
||||||||
Strategic Direction and Leadership |
|
||||||||
People Management |
|
||||||||
Program and Project Management |
|
||||||||
Financial Management |
|
||||||||
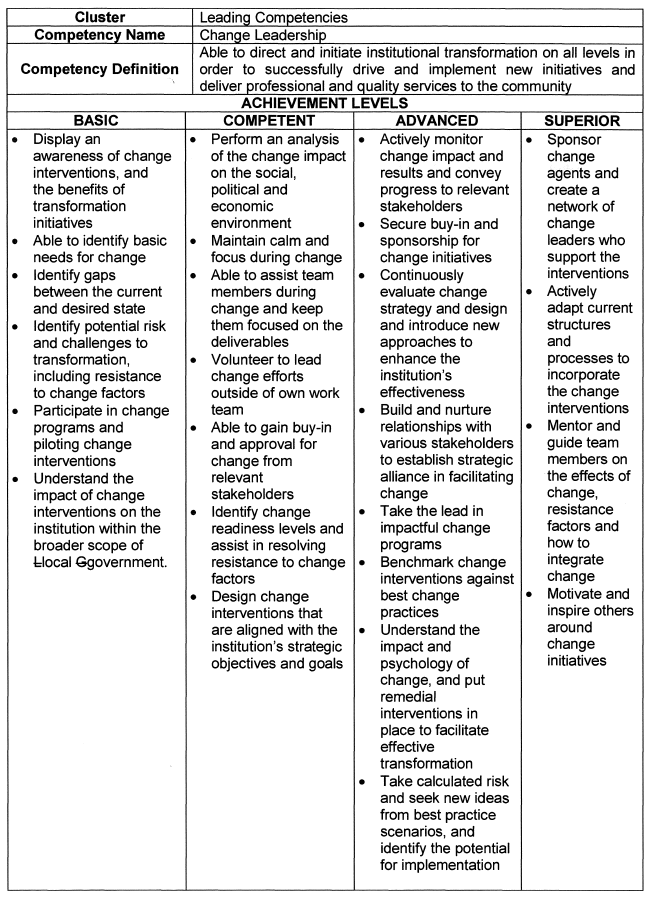
Change Leadership |
|
||||||||
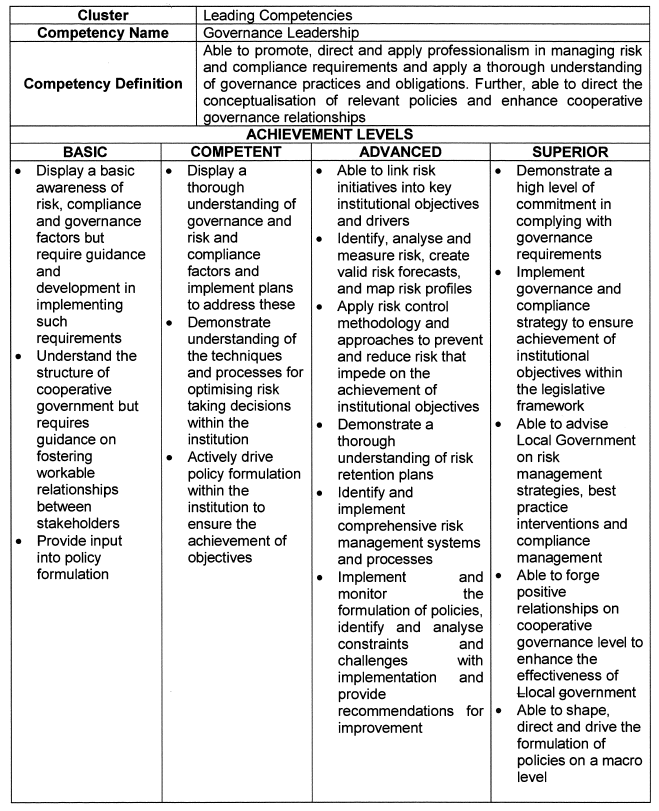
Governance Leadership |
|
||||||||
CORE COMPETENCIES |
|||||||||
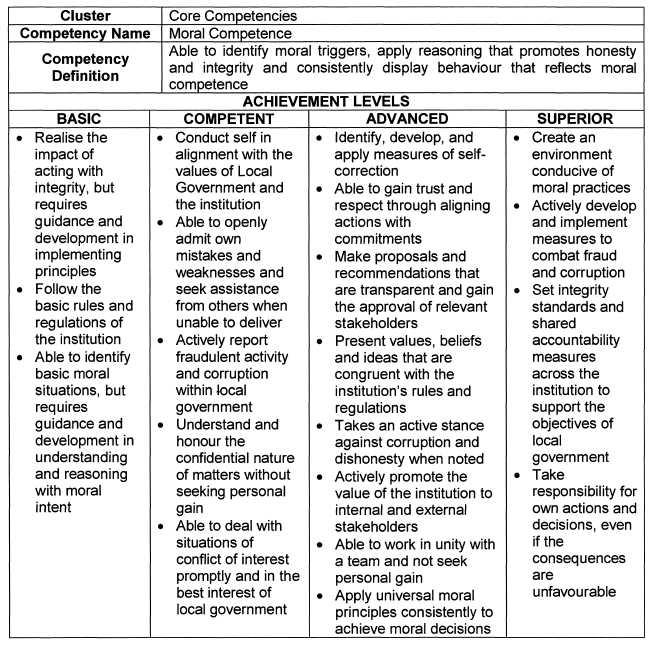
Moral Competence |
|||||||||
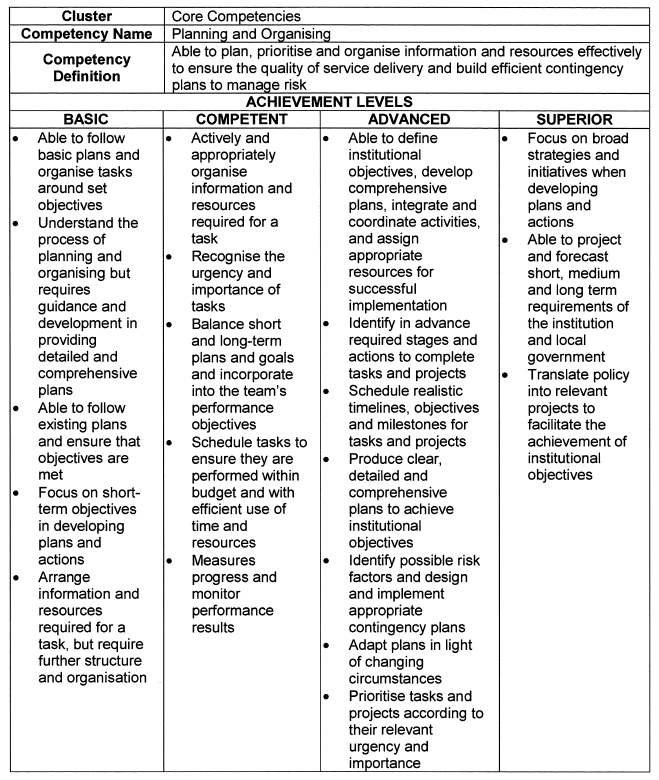
Planning and Organising |
|||||||||
Analysis and Innovation |
|||||||||
Knowledge and Information Management |
|||||||||
Communication |
|||||||||
Results and Quality Focus |
|||||||||
| 4. | Minimum Requirements |
The minimum requirements that accompany the competency framework, but do
not govern the selected competencies, as set out in annexure B to these
regulations, refer to the level of higher education qualification, work expereince
and knowledge that are needed to operate effectively in the local government
environment.
| 5. | Competency Descriptions |
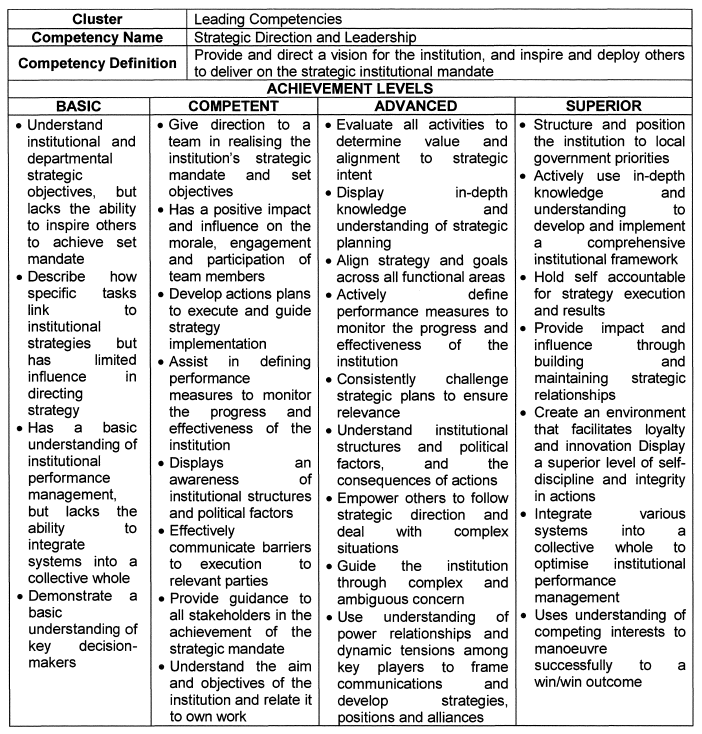
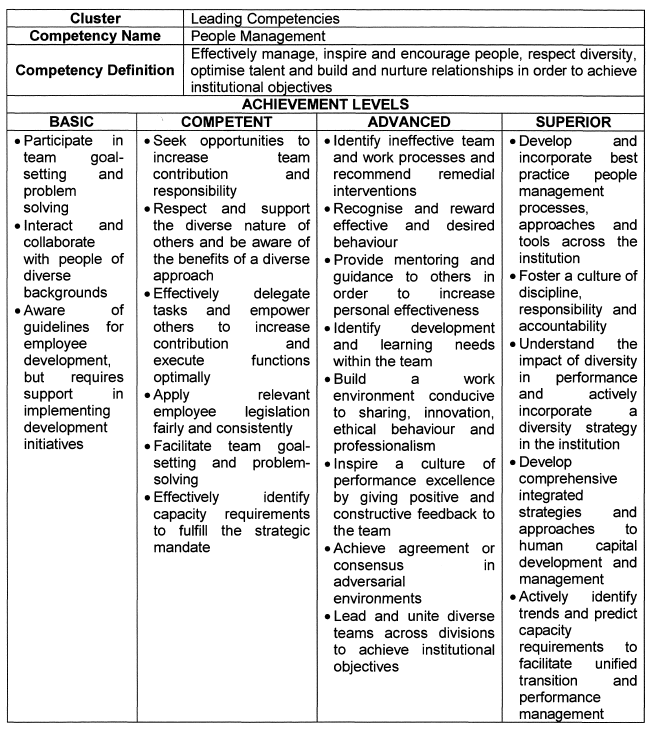
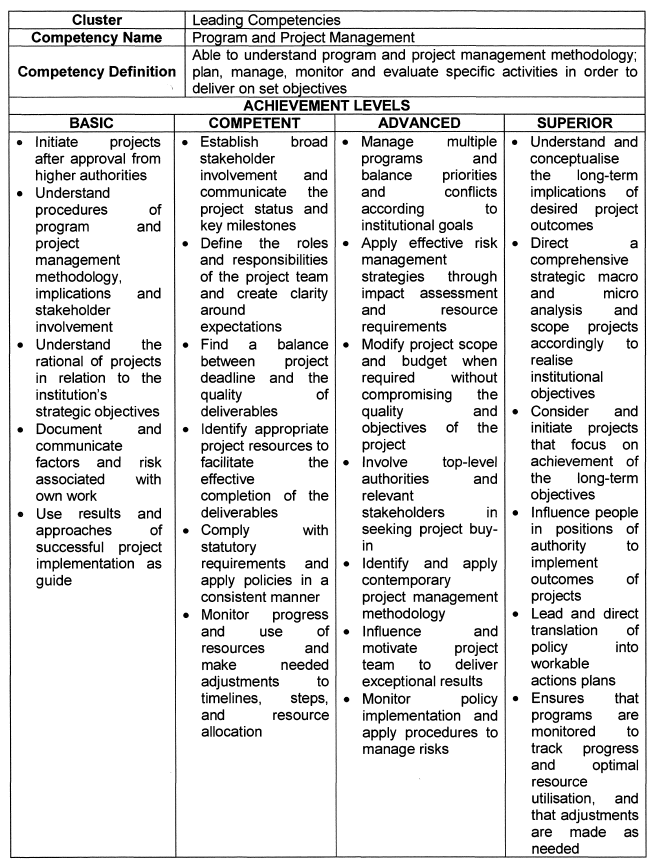
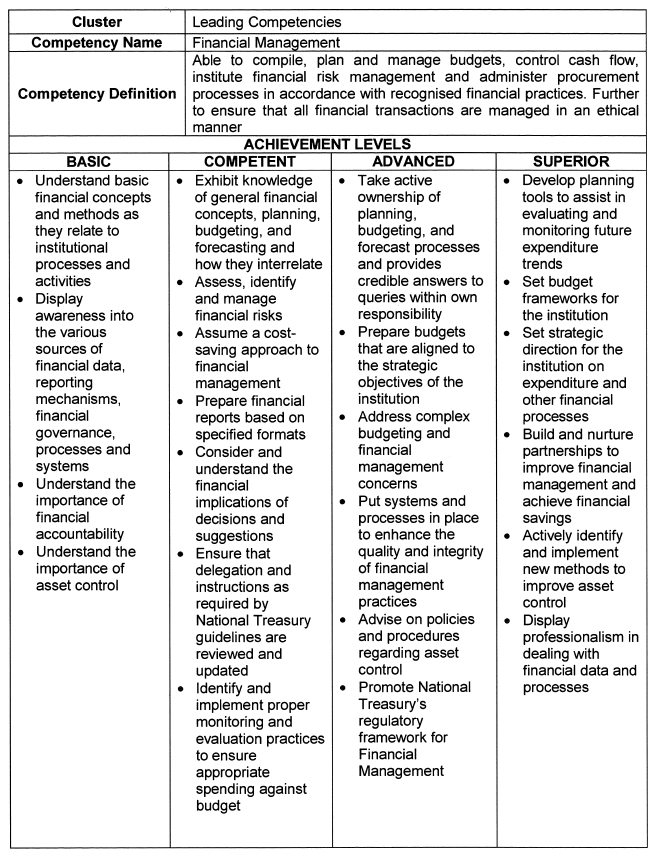
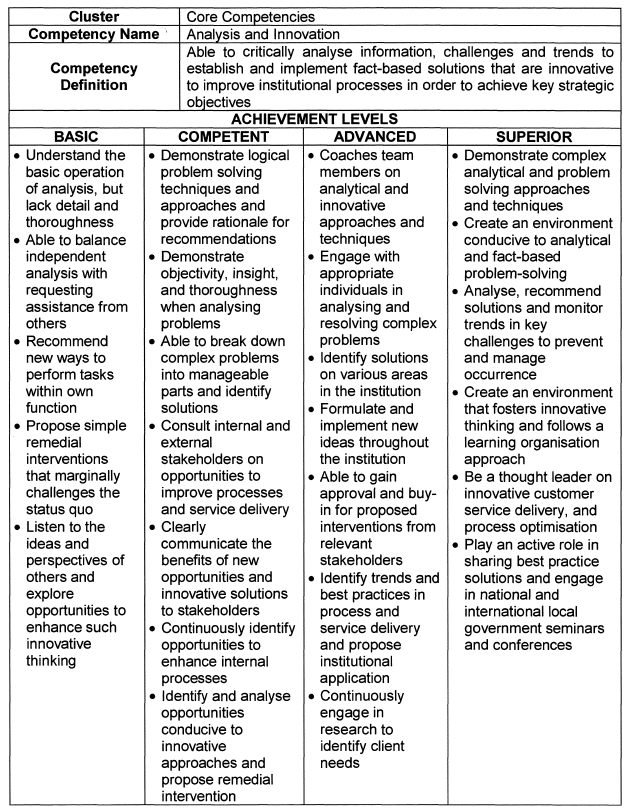
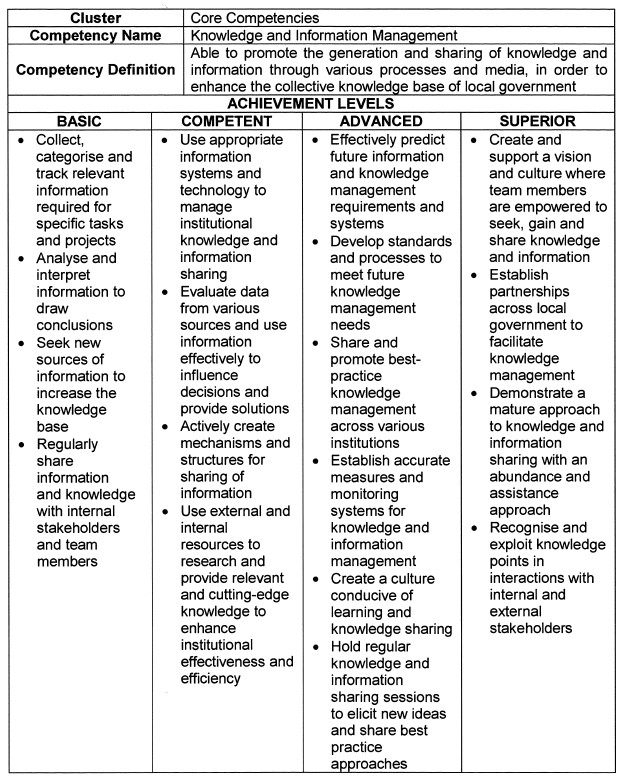
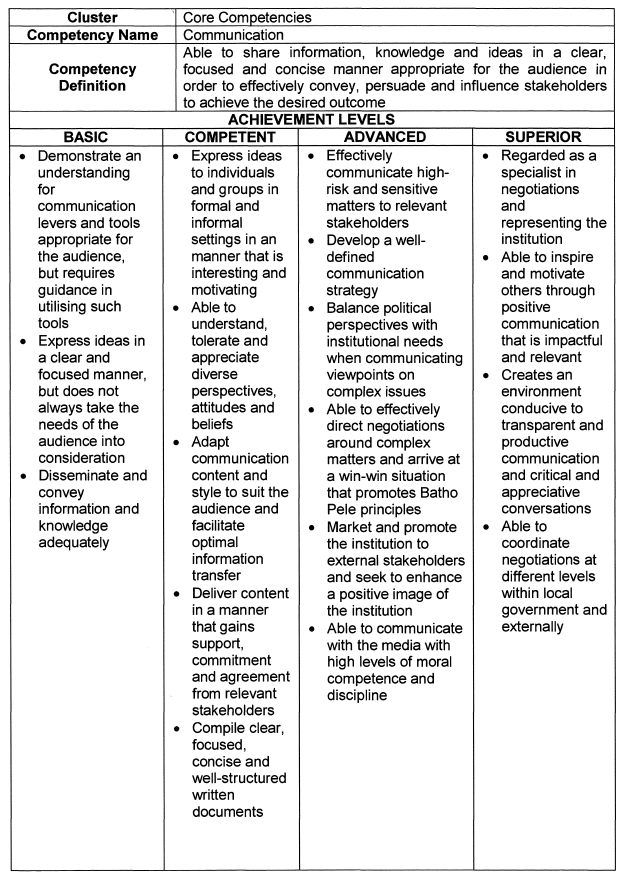
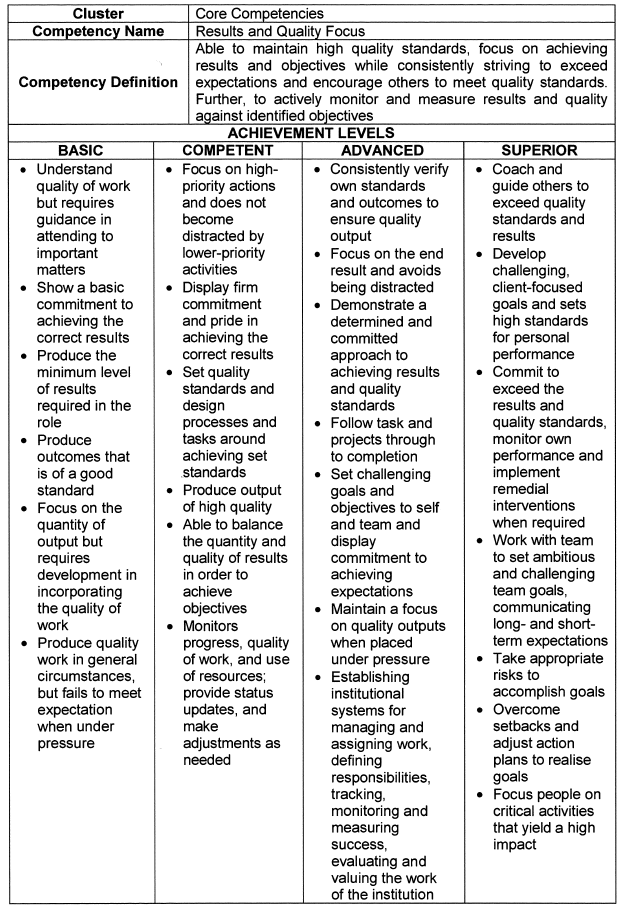
| 6. | Achievement Levels |
The achievement levels indicated in the table below serve as a benchmark for appointments, succession planning and development interventions.
| 6.1 | Individuals falling within the Basic range are deemed unsuitable for the role of senior manager, and caution should be applied in promoting and appointing such persons. |
| 6.2 | Individuals that operate in the Superior range are deemed highly competent and demonstrate an exceptional level of practical knowledge, attitude and quality. These individuals should be considered for higher positions, and should be earmarked for leadership programs and succession planning. |
Achievement Levels |
Description |
Basic |
Applies basic concepts, methods, and understanding of local government operations, but requires supervision and development intervention |
Competent |
Develops and applies more progressive concepts, methods and understanding. Plans and guides the work of others and executes progressive analyses |
Advanced |
Develops and applies complex concepts, methods and understanding. Effectively directs and leads a group and executes in-depth analyses |
Superior |
Has a comprehensive understanding of local government operations, critical in shaping strategic direction and change, develops and applies comprehensive concepts and methods |