


National Health Act, 2003 (Act No. 61 of 2003)NoticesNational Health Insurance Policy towards Universal Health CoverageChapter 1 : Introduction and Background1.3 International Context |
| 24. | South Africa is signatory to many international treaties and instruments, including the Universal Declaration of Human Rightsb and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR)c, in which the right of each individual to health and well being is enshrined. |
| 25. | More recently, the United Nations at its Seventieth General Assembly in September 2015 adopted seventeen (17) Sustainable Development Goals (SDG's) with 169 targets to be achieved over the next 15 years17. Goal 3 of the SDGs is aimed at ensuring healthy lives and promoting wellbeing for all at all ages. Target 3.8 on achieving UHC underpins all the other 9 targets of Goal 3. Goal 3.8 is specifically aimed at ensuring that countries achieve universal health coverage (UHC) through financial risk protection, access to quality essential healthcare services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines and vaccines for all. |
| 26. | Universal Health Coverage is an enabler for inclusive social protection systems18 and inclusive human development. It is about equity and is fundamental to providing social protection for health.The poorest populations usually face the highest health risks and need more health services. A UHC system aimed at providing healthcare coverage to all will ensure that all groups with a need in the population have access to these needed services19 without being exposed to financial hardships as shown in Figure 1: |
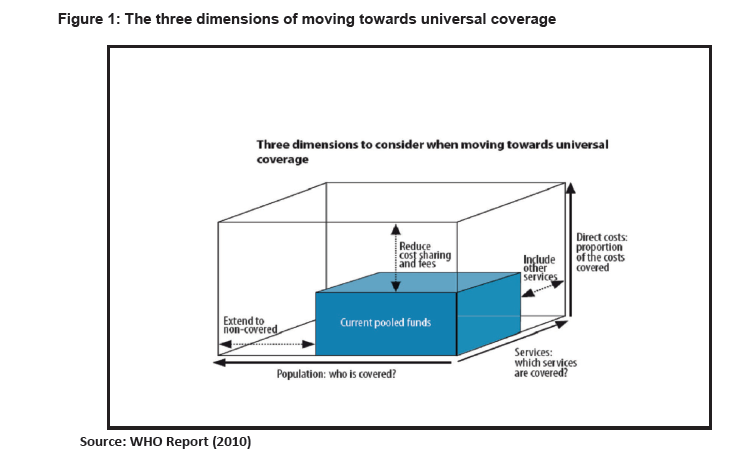
| 27. | Health financing within a UHC system needs to be specifically designed to provide all people with access to needed health services (including prevention, promotion, treatment and rehabilitation) of sufficient quality to be effective; and to ensure that the use of these services does not expose the user to financial hardship. A key element of financing for UHC is that the health costs for the poor and vulnerable are shared by the whole of society. Furthermore, the health care financing system should aim to spread the financial risks of illness across a wide population, by collecting large pools of prepaid funds that people can draw on to cover their health care costs at times of need, regardless of their ability to pay. |
| 28. | South Africa’s considered policy approach towards achieving UHC will be through the implementation of NHI. The conceptualisation and design of NHI will take into account the country’s experiences and global lessons learnt in the development of systems for UHC. |
______________________________________________________
| b | Adopted by the United Nations in 1948 |
| c | Adopted and opened for signature, ratification and accession by the General Assembly of the UN in 1966 and put into force in Jan 1976 |