| 1. | Terms defined in the Act |
In these regulations, any word or expression to which a meaning has been assigned in the Act, shall have the meaning so assigned.
| 2. | Terms not defined in the Act |
In these regulations, unless the context indicates otherwise:
| (i) | "absorbed dose" means the fundamental dosimetric quantity D expressed in the unit Jˑkg-1, termed the gray (Gy), defined as: |
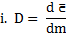
where 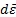 is the mean energy imparted by ionizing radiation to matter in a volume element and dm is the mass of matter in the volume element;
is the mean energy imparted by ionizing radiation to matter in a volume element and dm is the mass of matter in the volume element;
| (ii) | "assessment" means the process, and the result, of analysing systematically the hazards associated with sources and actions, and associated protection and safety measures, aimed at quantifying performance measures for comparison with criteria; |
| (iii) | "authorised" means permitted in writing by the Regulator; |
| (iv) | "authorised action" means an action authorised in terms of the National Nuclear Regulator Act, 1999 (Act No. 47 of 1999); |
| (v) | "average member of the critical group" means the individual receiving the average effective dose or equivalent dose (as applicable) in the critical group; |
| (vi) | "becquerel" (Bq) means the unit of radioactivity in nuclear transformations (or disintegrations) per second; |
| (vii) | "clearance" means removal of radioactive materials or radioactive objects within actions authorised by a nuclear installation licence, nuclear vessel licence or certificate of registration from any further control by the Regulator; |
| (viii) | "collective dose" means an expression for the total radiation dose incurred by a population, defined as the product of the number of individuals exposed to a source and their average radiation dose. The coIlective dose is expressed in person-sievert (person.Sv) (see collective effective dose); |
| (ix) | "collective effective dose" means the total effective dose incurred by a population, being the sum of all the individual effective doses to members of the population. Mathematically, the total effective dose to a population, S, is calculated as: |
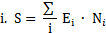
where E, is the average effective dose in the population subgroup i and N, is the number of individuals in the subgroup. It can also be defined by the integral:
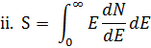
Where 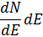 is the number of individuals receiving an effective dose between E and E+dE.
is the number of individuals receiving an effective dose between E and E+dE.
The collective effective dose Sk, committed by an event, a decision or a finite portion of an action k, during a time interval T, is given by:
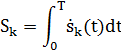 where
where 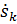 (t) is the collective effective dose rate at time t caused by k;
(t) is the collective effective dose rate at time t caused by k;
| (x) | "committed equivalent dose" means the quantity HT(T) defined as: |
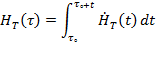
where to is the time of intake, HT(t), is the equivalent dose rate at time t in organ or tissue T and t is the time elapsed after an intake of radioactive substances. When t is not specified, it will be taken to be 50 years for adults and to age 70 years for intakes by children;
| (xi) | "critical group" means a group of members of the public which is reasonably homogeneous with respect to its exposure for a given radiation source and given exposure pathway and is typical of individuals receiving the highest effective dose or equivalent dose (as applicable) by the given exposure pathway from the given source; |
| (xii) | "decommissioning" means administrative and technical actions taken to allow the removal of all of the regulatory controls from a facility (except for a repository which is closed and not decommissioned); |
| (xiii) | "defence in depth" means the application of more than a single protective measure for a given radiation or nuclear safety objective, so that the objective is achieved even if one of the protective measures fails; |
| (xiv) | "discharge" means a planned and controlled release of radioactive nuclides to the environment; |
| (xv) | "disposal" means the emplacement of radioactive waste in an approved, specified facility without the intention of retrieval and "dispose of" has the corresponding meaning; |
| (xvi) | "dose" means the amount of radiation received, where the use of a more specific term such as "effective dose" or "equivalent dose" is not necessary for defining the quantity of interest; |
| (xvii) | "dose constraint" means a prospective and source-related restriction on the individual dose arising from the predicted operation of the authorised action which serves exclusively as a bound on the optimisation of radiation protection and nuclear safety: |
| (a) | to limit the range of options considered in the optimisation process, and |
| (b) | to restrict the doses via all exposure pathways to the average member of the critical group, in order to ensure that the sum of the doses received by that individual from all controlled sources remains within the dose limit, and which, if found retrospectively to have been exceeded, should not be regarded as an infringement of regulatory requirements but rather as a call for the reassessment of the optimisation of radiation protection. |
| (xviii) | "doselimit" means the value of effective dose or equivalent dose to individuals from actions authorised by a nuclear installation licence, nuclear vessel licence or certificate of registration, that must not be exceeded; |
| (xix) | "effective dose" means the quantity E expressed in the unit J-kg1, termed the sievert (Sv), defined as the summation of the tissue equivalent doses, each multiplied by the appropriate tissue weighting factor— |
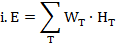
where HT is the equivalent dose in Tissue T and WT is the tissue weighting factor for tissue T, from the definition of equivalent dose, it follows that:
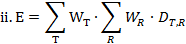
where WR is the radiation weighting factor for radiation R and DTR is the average absorbed dose in the organ or tissue T;
| (xx) | "emergency planning" means the process of developing and maintaining the capability to take actions that will mitigate the impact of an emergency on persons, property or the environment; |
| (xxi) | "emergency preparedness" means the capability to promptly take actions that will effectively mitigate the impact of an emergency on persons, property or the environment; |
| (xxii) | "emergency response" means the performance of actions to mitigate the impact of an emergency on persons, property or the environment; |
| (xxiii) | "equivalent dose" means the quantity HTR expressed in the unit J kg", termed the sievert (Sv) defined as— |
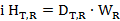
where DTR is the absorbed dose delivered by radiation type R averaged over a tissue or organ T and WR is the radiation weighting factor for radiation type R; when the radiation field is composed of different radiation types with different values of WR; the equivalent dose is:
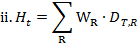
| (xxiv) | "environmental monitoring" means the measurement of external dose rates due to sources in the environment and of radioactive nuclide concentrations in environmental media; |
| (xv) | "exclusion" means exclusion from the scope of regulatory control; |
| (xvi) | "exemption" means the determination by the regulator that an action need not be subject to some or all aspects of regulatory control on the basis that the exposure (or potential exposure) due to the action is too small to warrant the application of those aspects; |
| (xvii) | "exposure" means the act or condition of being subject to irradiation; |
| (xviii) | "exposure pathway" means a route by which radioactive material can reach or irradiate humans; |
| (xxix) | "fertile" means nuclear material which can be converted into material which is capable of nuclear fission; |
| (xxx) | "fissile" means material that undergo fission by neutrons of all energies; |
| (xxxi) | "LAEA" means the International Atomic Energy Agency; |
| (xxxii) | "individual monitoring" means monitoring using measurements by equipment worn by individual workers, or measurements of quantities of radioactive materials in or on their bodies; |
| (xxxiii) | "institutional control" means control of a waste site (for example, disposal site) by a statutory authority or institution; this control may be active (monitoring, surveillance, remedial work) or passive (land use control) and may be a factor in the design of a nuclear facility (for example, near surface disposal facility); |
| (xxxiv) | "intake" means the process of taking radioactive nuclides into the body by inhalation or ingestion or through the skin; |
| (xxxv) | "monitoring" means the continuous or periodic measurement of radiological and other parameters or determination of the status of a system; |
| (xxxvi) | "normal operational exposure" means an exposure which is expected to be received under normal operating conditions, including possible minor mishaps that can be kept under control; |
| (xxxvii) | "nuclear safety" means the achievement of safe operating conditions, prevention of nuclear accidents or mitigation of nuclear accident consequences, resulting in the protection of workers, the public and the environment against the potential harmful effects of ionizing radiation or radioactive material; |
| (xxxviii) | "occupational exposure" means exposure of a worker in the course of his or her work in excess of an annual effective dose of 1 mSv in addition to natural background radiation, and "occupationally exposed" has the corresponding meaning; |
| (xxxix) | "operational safety assessment" means a safety assessment undertaken during operations; |
| (ixl) | "prior safety assessment" means a safety assessment undertaken prior to commencement of operations; |
| (xli) | "radiation" means ionising radiation; |
| (xlii) | "radiation protection" means the protection of people from the effects of exposure to ionising radiation, and the means for achieving this; |
| (xliii) | "radiation weighting factor" means a multiplier of absorbed dose used for radiation protection purposes to account for the relative effectiveness of different types of radiation in inducing health effects, the value of which is that specified in the IAEA International Basic Safety Standards for Protection against Ionizing Radiation and for the Safety of Radiation Sources; |
| (xliv) | "radioactive waste" means any material, whatever its physical form, remaining from an action requiring a nuclear installation licence, nuclear vessel licence or certificate of registration and for which no further use is foreseen, and that contains or is contaminated with radioactive material and does not comply with the requirements for clearance; |
| (xlv) | "radioactive waste acceptance criteria" means the quantitative or qualitative criteria, specified by the operator and approved by the regulator, for radioactive waste to be accepted by the operator of a repository for disposal, or by the operator of a storage facility for storage; |
| (xlvi) | "radon" means the isotope 222Rn of the element of atomic number 86; |
| (xlvii) | "registration" means the granting of a certificate of registration; |
| (xlviii) | "risk" means (qualitatively expressed) the probability of a specified health effect occurring in a person or group as a result of exposure to radiation or (quantitatively expressed) a multi-attribute quantity expressing hazard, danger or chance of harmful or injurious consequences associated with actual or potential exposures relating to quantities such as the probability that specific deleterious consequences may arise and the magnitude and character of such consequences; |
| (xlix) | "risk assessment" means an assessment of the radiological risks associated with normal operation and potential accidents involving a source or action; |
| (l) | "safety assessment" means an analysis to evaluate the performance of an overall system and its impact, where the performance measure is radiological impact or some other global measure of impact on safety; |
| (li) | "safety culture" means the assembly of characteristics and attitudes in organizations and individuals which establishes that, as an overriding priority, protection and safety issues receive the attention warranted by their significance; |
| (lii) | "source" means anything that may cause radiation exposure, such as by emitting ionising radiation or releasing radioactive substances or materials; a complex or multiple installation situated at one location or site may, as appropriate, be considered as a single source for the purposes of application of these regulations; |
| (liii) | "storage" means the holding of spent (used) nuclear fuel or radioactive waste in a facility that provides for its containment, with the intention of retrieval; |
| (liv) | "the Act" means the National Nuclear Regulator Act, 1999 (Act No. 47 of 1999); |
| (lv) | "tissue weighting factor" means a multiplier of the equivalent dose to an organ or tissue used for radiation protection purposes to account for the different sensitivities of different organs and tissues to the induction of stochastic effects of radiation, the value of which is that specified in the IAEA International Basic Safety Standards for Protection against Ionizing Radiation and for the Safety of Radiation Sources; |
| (lvi) | "workplace monitoring" means monitoring using measurements made in the working environment. |



![]()
![]() is the mean energy imparted by ionizing radiation to matter in a volume element and dm is the mass of matter in the volume element;
is the mean energy imparted by ionizing radiation to matter in a volume element and dm is the mass of matter in the volume element;![]()
![]()
![]() is the number of individuals receiving an effective dose between E and E+dE.
is the number of individuals receiving an effective dose between E and E+dE.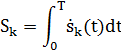 where
where ![]() (t) is the collective effective dose rate at time t caused by k;
(t) is the collective effective dose rate at time t caused by k;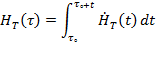
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()