


National Health Act, 2003 (Act No. 61 of 2003)NoticesNational Health Insurance Policy towards Universal Health CoverageChapter 7 : Financing of NHI7.3 NHI Expenditure Projections: and Cost Estimates7.3.2 Estimates of Public and Private Health Expenditure |
| 209. | South Africa spent approximately 8.6 per cent of GDP on health services in 2013/14, with an annual average real increase in spending of 1 per cent a year over the past three years (Table 2). |
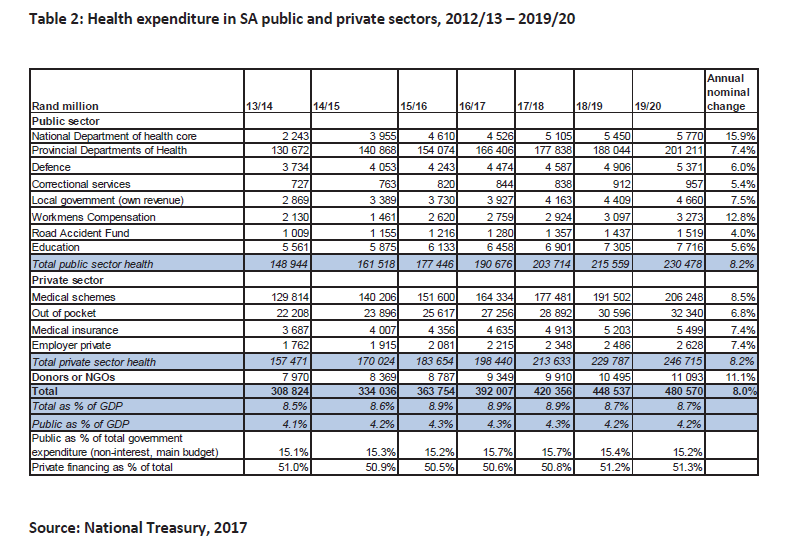
| 210. | Within the estimated health expenditure total for 2016/17, 4.3 per cent of GDP (R190.7 billion) was accounted for in the public sector, 4.4 per cent of GDP through private financing streams (R198.4 billion) and 0.2 per cent through donors. The largest public spending is by provincial Departments of Health at 3.8 per cent of GDP and the largest private spending channel is through medical schemes (3.7 per cent of GDP). |
| 211. | The table above shows the total spending in the health system (public and private). The private sector health expenditure by medical schemes in 2016/17 is estimated at R164.3 billion. This amount includes preliminary estimates of R20 billion which is the State’s contribution to some medical schemes as a subsidy for state employees (This figure excludes contributions by the state to Polmed, Parmed and State-owned entities). The Medical Tax Credit provides a tax credit to individuals for their own contributions and contributions on behalf of dependents to medical schemes. The tax revenue foregone for this purpose amounted to R18.5 billion in 2014/15, covering workers employed in the public and private sector. These amounts are not available for the uninsured population. |